Brushed motor vs brushless motors
If you are new to the world of radio control, or are just out of touch with the new technology, you may not know the differences between conventional brushed and brushless motor systems. I have written this guide to help other radio control enthusiasts understand the differences between the two.
In a nutshell, brushless motors offer more power and higher efficiency than the equivalent brushed motor of the same size. You’ll get longer run times and higher speeds with a brushless motor of the same physical size, and very little maintenance is required with the brushless type.
The basics
The internal workings of both brushed DC (direct current) and brushless DC motors are based on the same idea; the motor windings have current supplied to them and an electromagnetic field is generated, which pushes/repels against the permanent magnets and causes the shaft to turn. As the shaft turns, this pushing energy transfers from one set of windings to the next causing the motor shaft to rotate continuously.
The differences between the two motor types are listed below, as well as the advantages and disadvantages.
Brushed RC Motors
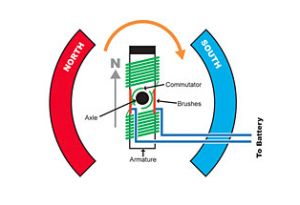
With a brushed motor, the windings are fixed onto the central shaft inside the motor case and spin with the shaft when current is applied. The permanent magnets don’t move – they are fixed to the inside of the motor can. Power is supplied to the motor windings by two brushes (positive and negative) that push against the commutator on the central shaft. The friction between the brushes and the commutator is the reason why this motor is not as efficient as a brushless motor. Also, the brushes and commutator will wear out after some time, so brushed motors require maintenance and replacement parts from time to time. A more powerful brushed motor will wear out quicker than a slower one.
If you have ever owned a ready-to-run electric rc car, chances are that you would have used a brushed rc motor at some point. Due to their affordability, brushed motors are usually supplied with most entry-level to mid-range radio control car kits. The extremely popular Tamiya kits, for example, are usually supplied with a standard 540 type silver can.
The brushed DC motor goes back to the mid 1800’s and it was this type of motor that first appeared in the early radio controlled car kits.
Advantages of a brushed RC Motor:
Inexpensive – brushed motors are cheaper to produce
Simple wiring – brushed motors only require two wires to power them and don’t require any electronic commutation. Therefore, brushed Electronic Speed Controllers (ESC) are relatively inexpensive.
Disadvantages of a brushed RC Motor:
Brushes and commutator wear out after time, although they are rebuildable in some motors.
Not very efficient when compared to brushless. More power is wasted through the additional heat loss and friction of the brushes against the commutator. This means you will have shorter run times.
Brushless Motors
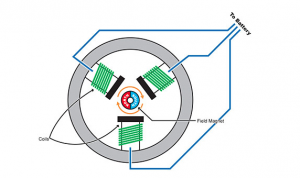
The brushless motor doesn’t require a physical commutator; this is one of the reasons they are so popular today. No commutator or brushes means almost zero maintenance (the bearings will last a very long time but obviously not forever).
You’ll find a brushless motor system in the more expensive ready-to-run cars, and most serious racers will use this type of motor, if permitted.
Brushless motor technology was invented in the 1960’s but didn’t really become available for radio controlled cars until around 2003-2004 (earlier for model aircraft).
Advantages of a brushless RC Motor:
Very low maintenance; no brushes or commutator to wear out.
Higher efficiency compared to brushed so you’ll get longer run times.
Higher speeds are achievable.
Disadvantages of a brushless RC Motor:
More expensive to buy.
A more complicated ‘Brushless ESC’ (Brushless Electronic Speed Controller) is required. to power it.





